
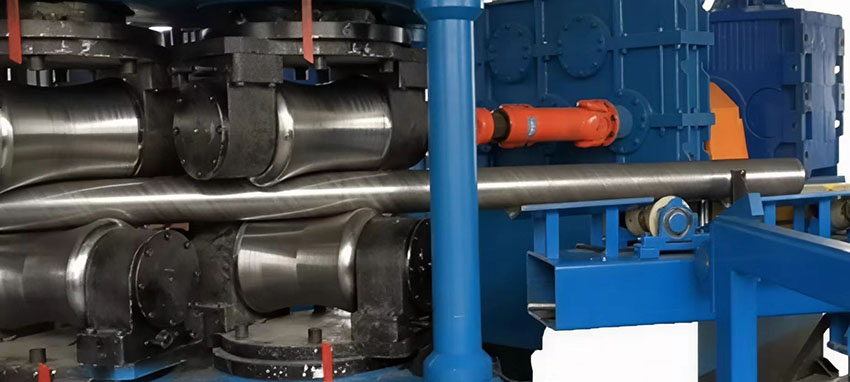
 Generally, there are two rows of straightening rollers, the number of which varies. The pipe straightening machine utilizes the continuous action of multiple sets of straightening rollers to plastically deform and correct the pipe. As the pipe passes through the rollers, it undergoes repeated bending and reverse loading, gradually eliminating internal residual stress and original curvature. By adjusting roller spacing, pressure angle, and compression depth, the machine restores straightness by operating at the critical state between elastic and plastic deformation. High-precision models integrate detection feedback systems to monitor pipe deformation in real-time and dynamically adjust parameters, ensuring uniform straightening.
Generally, there are two rows of straightening rollers, the number of which varies. The pipe straightening machine utilizes the continuous action of multiple sets of straightening rollers to plastically deform and correct the pipe. As the pipe passes through the rollers, it undergoes repeated bending and reverse loading, gradually eliminating internal residual stress and original curvature. By adjusting roller spacing, pressure angle, and compression depth, the machine restores straightness by operating at the critical state between elastic and plastic deformation. High-precision models integrate detection feedback systems to monitor pipe deformation in real-time and dynamically adjust parameters, ensuring uniform straightening.



